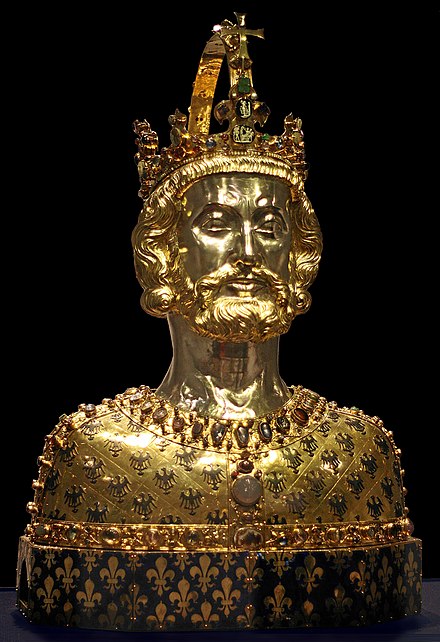
King

| Part of a series on |
| Imperial, royal, noble,gentry and chivalric ranks in Europe |
|---|
 |
King is a royal title given to a male monarch.[1] In a modern context, the title may refer to the ruler of one of a number of modern monarchies (either absolute or constitutional).[2][3] A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. The title of king is used alongside other titles for monarchs: in the West, emperor, grand prince, prince, archduke, duke or grand duke, and in the Islamic world, malik, sultan, emir or hakim, among others.[4]
The term king may also refer to a king consort, a title that is sometimes given to the husband of a queen regnant, but the title of prince consort is more common.
Etymology
The word king traces back to late Old English cyning, meaning "ruler" or "leader," derived from Proto-Germanic kuningaz. This root also gave rise to similar terms across other Germanic languages, such as Dutch koning, Old Norse konungr, Danish konge, and German König. The precise origin of "kuningaz" remains uncertain, but it may be linked to Old English cynn ("family, race"), suggesting that a king was originally viewed as the "leader of the kin" or "head of the people." Another theory proposes that the term referred to one "of noble descent," connecting kingship with divine or aristocratic lineage. Linguists and historians have long debated the social and ideological meanings behind this relationship between king and kin, though the linguistic connection is widely accepted.[5]
Current kings
| Part of the Politics series |
| Monarchy |
|---|
 |
 Politics portal Politics portal |
Currently (as of 2023), eighteen kings are recognized as the heads of state of sovereign states. Most of these kings serve as heads of state in constitutional monarchies. However, those ruling over absolute monarchies include the King of Saudi Arabia and the King of Eswatini.[6][7]
See also
- Anointing
- Big man (anthropology)
- Buddhist kingship
- Client king
- Coronation
- Designation
- Divine right of kings
- Germanic kingship
- Great King
- High King
- King consort
- King of Kings
- Petty king
- Queen
- Realm
- Royal and noble ranks
- Royal family
- Sacred king
- Tribal kingship
- Khan
- Archon
- Basileus
- Lugal
- Kabaka
- Mepe (title)
- Malik/Melekh
- Mwami
- Negus
- Oba
- Raja
- Yang di-Pertuan Agong
- Rex (king)
- Rí
- Tlatoani
- Shah
- Tagavor
Notes
- ^The definition of King from the OED
- ^Bogdanor, Vernon (1995). The Monarchy and the Constitution. Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-19-829334-7.
- ^Kimizuka, Naotaka (July 2024). Constitutional Monarchy of the Twenty-First Century. Springer. ISBN 978-981-97-4327-8.
- ^Pine, L.G. (1992). Titles: How the King became His Majesty. New York: Barnes & Noble. p. 86. ISBN 978-1-56619-085-5.
- ^"Search 'king' on etymonline".
- ^"Saudi Arabia: Country Profile".
- ^"Africa's Eswatini, one of the last absolute monarchies, holds an election without political parties". Associated Press News. 29 September 2023.
References
- Cannadine, David; Price, Simon, eds. (1987). Rituals of Royalty: Power and Ceremonial in Traditional Societies. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-33513-2. LCCN 86-29881.
- Craughwell, Thomas J. (2009). 5,000 Years of Royalty: Kings, Queens, Princes, Emperors & Tsars. Black Dog & Leventhal Publishers. ISBN 978-1-60376-189-5.
- Hani, Jean (2011). Sacred Royalty: From the Pharaoh to the Most Christian King. The Matheson Trust. ISBN 978-1-908092-05-2.
External links
 Media related to Kings at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Kings at Wikimedia Commons
- Phillip, Walter Alison (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). pp. 805–806.


.jpg/440px-King_Charles_III_(July_2023).jpg)
















.jpg/440px-King_Philippe_of_Belgium_(January_2025).jpg)



.jpg/440px-King_Norodom_Sihamoni_(2019).jpg)



.jpg/440px-Mswati_III_in_Yokohama_(cropped).jpg)

.jpg/440px-King_Abdullah_II_(cropped).jpg)





_(cropped).jpg/440px-Pedro_Sánchez_se_reúne_con_el_rey_de_Marruecos,_Mohamed_VI_(1)_(cropped).jpg)





_(cropped).jpg/440px-Salman_of_Saudi_Arabia_-_2020_(49563590728)_(cropped).jpg)



_(cropped).jpg/440px-Carl_XVI_Gustaf_of_Sweden_2018_(42282165922)_(cropped).jpg)